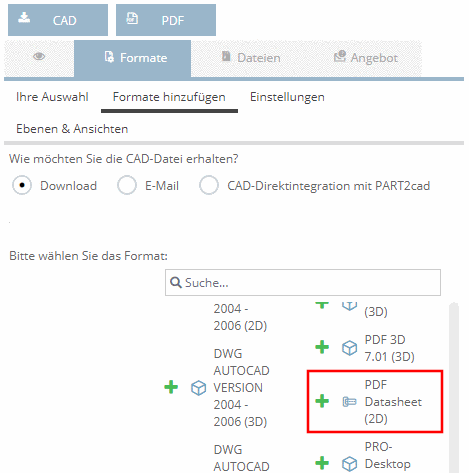
When using value range variables you can also use an Attribute algorithm in addition. A frequent application is the use of an IF condition, to make the value range conditional upon the value of a certain variable.
In the following example the value range of L shall be displayed depending on the value of FORM (or FORM1). For "Rounded edges" [1:6000], for "Sharp edges" [1:2000].
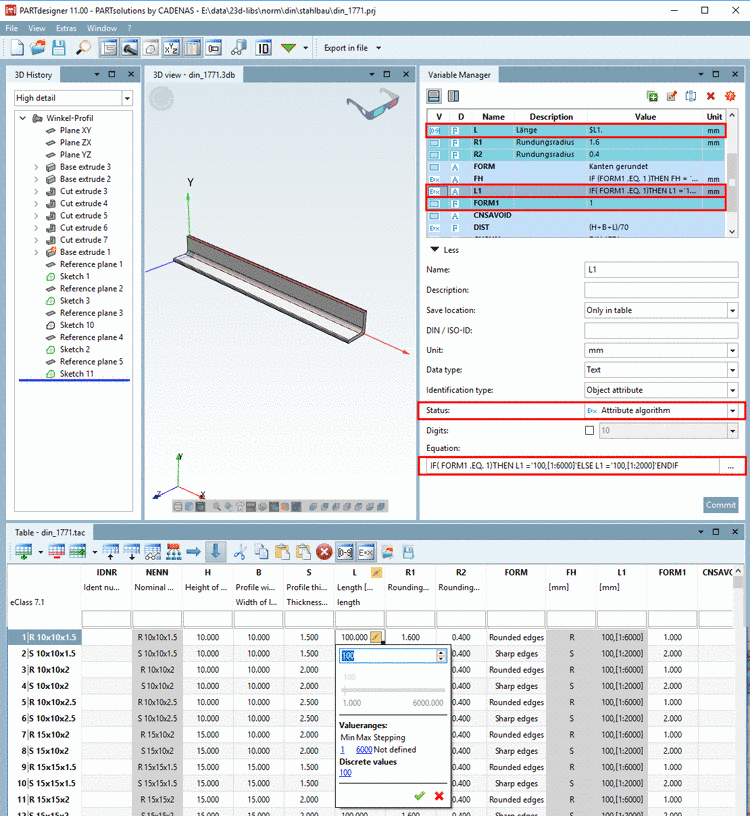
For this an attribute algorithm has been used for the variable L1 (not displayed in PARTdataManager):[97]
IF( FORM1 .EQ. 1) THEN L1 ='100,[1:6000]' ELSE L1 ='100,[1:2000]' ENDIF
If the variable FORM1 has the value 1, then the value range of L1 is from 1 to 6000 with a default value of 100, otherwise the value range is from 1 to 2000.
The figure shows the selected variable "L1" with Status "Attribute algorithm" in the Variable Manager.[98]
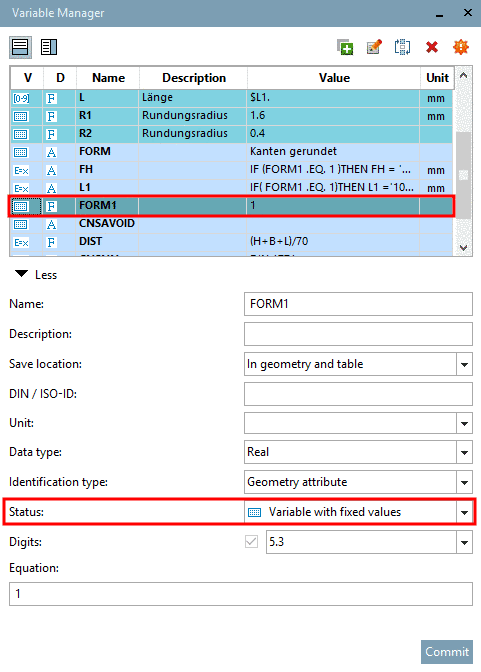
The variable FORM1 is a Variable with fixed values. In this example here, it has the value 1 or 2. On this variable, the condition is focused.
The variable L is defined as Value range variable. It references the variable L1, which contains the attribute algorithm (see above).